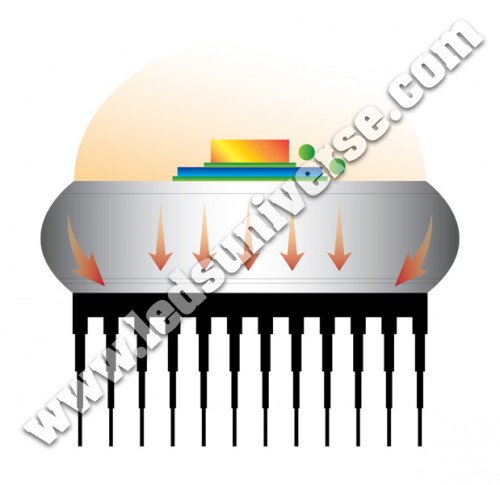
LED Technology has evolved a lot over the last couple of years to new lengths. Recently LedsUniverse has helped pushing this breakthrough even further by developing a channel or passageway between the junction and the heating sink, which allows the LEDs to be driven even to higher power without affecting their life span.
Therefore we would like to explain you in layman’s terms how this “bridge” will contribute positively to a better resistance against heat. In order to do that, it is necessary to start with some basic concepts.
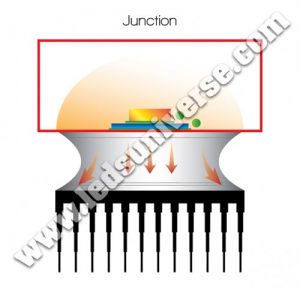
1. What is the Junction?
The junction is the part of the LED light where the chip is located.
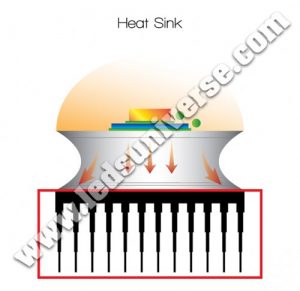
2. What is the Heat Sink?
The sink is a passive heat exchanger that receives the heat generated inside the chip compartment, helping cooling down the junction section. The heat sink is valuable to the fixture due to its heat dissipation ability, as the front compartment is insufficient to moderate the overall temperature in its own. The heat sink is located on the back of the lamp.
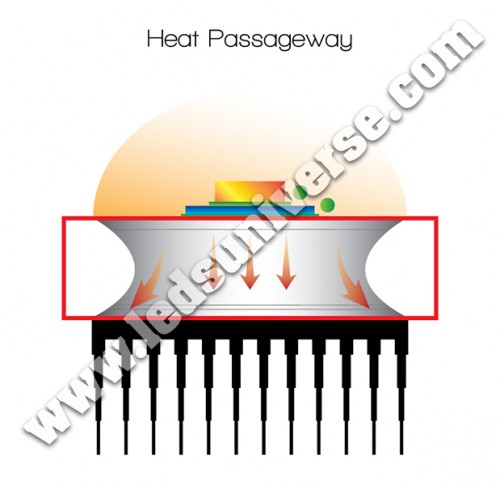
3. What is the Heat Passageway?
The passageway is the channel that connects the junction with the heat sink. In this short explanation, and for more illustrative purposes, we refer to it as merely a channel; however, in optometry the components of this “bridge” include parts such as the Base Plate, the Solder Point, the Dielectric and Metal Cored PCB. The installation and rearrangement of those components will have an impact in this “channel”.

4. How Has LedsUniverse Revolutionized the Heat Dissipating Process?
Up until now, most LED lights would get very hot in the front because the heat could not travel fast enough to the heat sink. This occurred mainly because the passageway was too narrow and had a concave shape.
Therefore, our engineers researched and developed a new way of structuring the elements within the passageway in such a way that it would allow the walls to be straight and linear. As a consequence, the heat flows faster from the junction to the sink, and under this new perspective, the power can be driven higher.
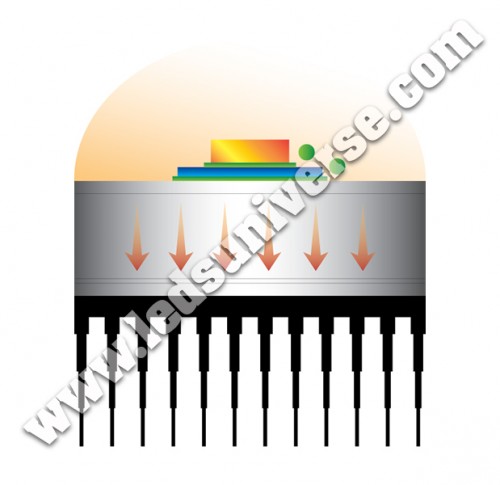
Inside of the chip compartment the temperature of our lights never exceeds 150 degrees Celsius, but in order to achieve this, we were able to successfully redirect the “extra” heat to the sink, whose temperature is around 80 to 90 degrees Celsius.
Now the junction remains cooler whereas the excess heat will be driven to the light’s rear (or the sink), which becomes hotter. However, as the sink is produced with pressed aluminum material, the light won’t suffer any damage.

5. What can the Future Bring to Heat Dissipation?
In the past the LED got very hot in the front, but cooler in the back. Now, the paradigm has changed.
The future of high power LED lies on the following motto: cooler in the front and hot in the back. In order to achieve this goal, LedsUniverse R&D team will try to reshape the passageway chamber into a convex shape.